

Systèmes, pivot de Gauss, matrices, opérations matricielles, déterminant, inverse matricielle, polynôme caractéristique, valeurs propres, vecteurs propres, espaces propres, diagonalisation
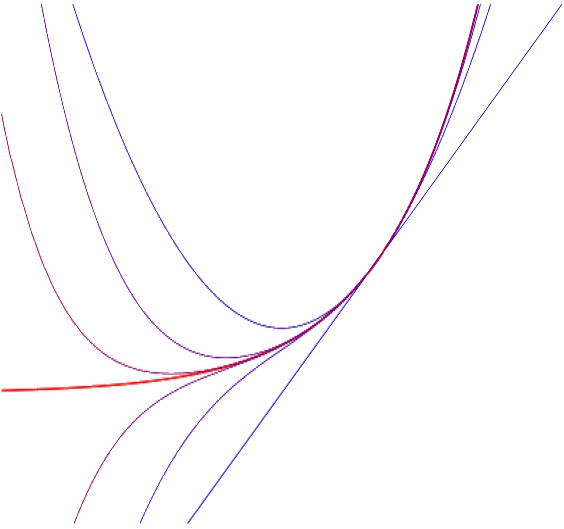
Etude locale, Formules de Taylor, Maclaurin, Développement limité, fonctions a plusieurs variable, ligne de niveau, gradient, point critique, hessienne, moindre carré

Cours co-écrit avec Yannick Henrio, Langages, Langages rationnels, REGEX, Expressions régulières, automates, détermination, epsilon-transition
Chiffrements monoalphabétiques : césar, affine, substitution. Attaque en brute force. Attaque fréquentielle. Chiffrement de Hill. Chiffrement de Vigenére et attaque de Kasiski. Chiffrement DES. Chiffrement RSA.
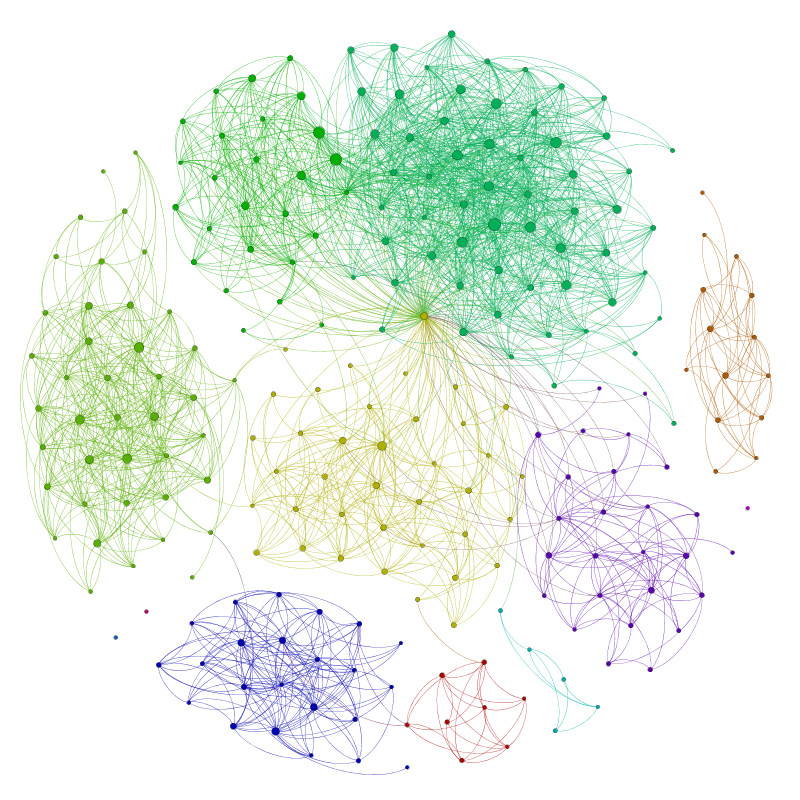

Graphes orientés, non orientés, standards. Représentation sagittale et matricielle. Arbres. Forêts. Chaines. Circuits. Successeurs. Prédécesseurs. Descendants. Ascendants. Connexité. Degrés. Coloration. Plus court chemin. Numérotation. Théorie des jeux. Mot et langages. Automates.

Matrice, système, suites, diagonalisation, équation différentielle, déterminant

Calculs propositionnelles. Théorie des ensembles. Prédicats et quantificateurs. Algèbre de Boole. Relation binaire (interne). Sommations finies.
Algèbre booléenne, suites, séries, intégrales

Cours co-écrit avec A. Nassiet Produit scalaire, norme, projection,

Variations de suites, limites de suites, suites arithmétiques, suites géométrique, suites arithmético-géométrique, suite homographique, point fixe, suites équivalentes
Trigonométrie, équation trigonométrique, inéquation trigonométrique, nombre complexe, forme cartésienne, forme polaire, formule d'Euler, géométrie, racine carré de nombre complexe, calcul intégrale, intégration par partie, série de Fourier, Dirichlet, Parseval, Epicycloïde
Problème linéaire en dimension 2, fonction à une variable (dérivation, variation, ...), fonctio à deux variables (ligne de niveau, fonction partielle, dérivés partielles, gradients, point critique, matrice hessienne).

Probabilités discrètes, probabilités continues, variables aléatoire, estimateur, statistique en dimension 1, 2 et $n$. Modélisation linéaire. Régression linéaire. Régression linaire multiple. Paradoxe de Simpson
Problème linéaire. Représentation graphique. Méthode du simplexe. Méthode des deux phases. Méthode du grand M. Problème dual. Optimisation de flot. Flux. Algorithme de Ford-Fulkerson. Affectation. Algorithme hongrois.

De $\mathbb{N}$ à $\mathbb{R}$. Equations. Inéquations. Polynômes. Systèmes. Statistiques. Fonctions. Limites. Dérivées. Asymptotes. TVI. Suites. Logarithme. Exponentielle. Intégrales. Probabilités. Variables aléatoires. Trigonométrie. Nombres complexes. Géométrie.
Cours rédigé par Haïfa Zargayouna
SAE du BUT STID rédigée par Haïfa Zargayouna

SAE du BUT STID rédigée par Pierre GERARD

Cours rédigé par Pierre GERARD